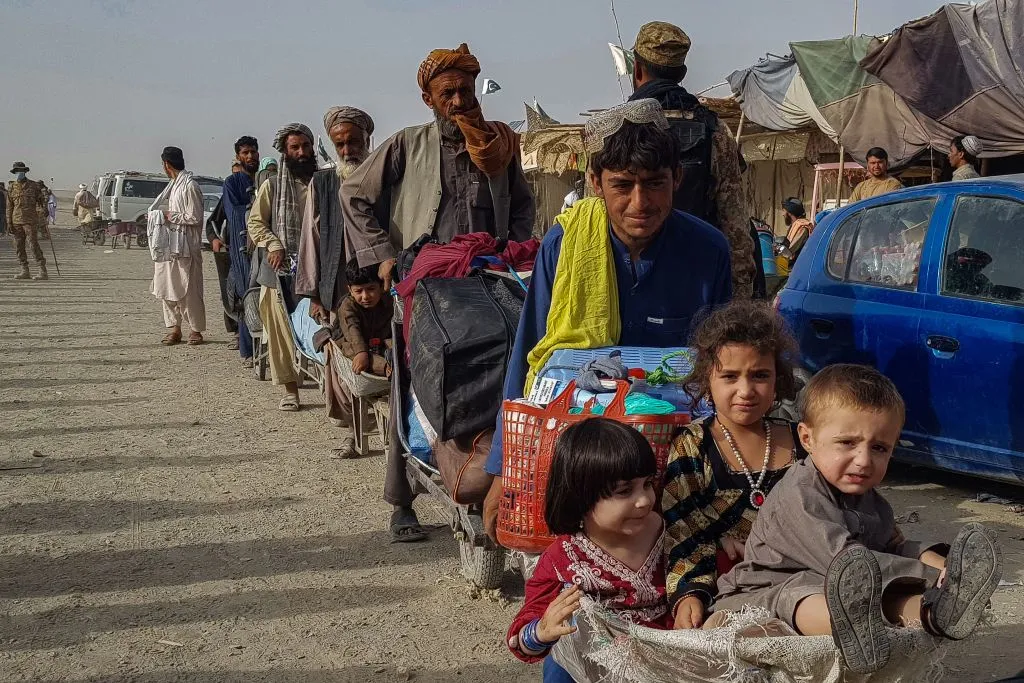
On October 3, the apex committee of the Pakistan government announced a deadline of November 1 for all undocumented immigrants to leave the country.
Since this decision will affect a large number of undocumented Afghans living in Pakistan, it is already being seen as a major jolt to an already struggling bilateral relationship.
The history of Afghan refugees in Pakistan is a long and complex one, spanning several decades. The influx of Afghan refugees into Pakistan can be traced back to the late 1970s when Afghanistan was engulfed in a series of conflicts and war.
Here is a brief overview of the key events in the history of Afghan refugees in Pakistan.
Soviet Invasion (1979): The major wave of Afghan refugees began with the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan in 1979. Millions of Afghans fled their homeland to escape the violence and persecution. Pakistan, due to its proximity to Afghanistan and cultural ties, became one of the primary destinations for Afghan refugees.
Refugee Camps: Pakistan set up refugee camps along the border with Afghanistan to provide shelter, food, and basic services to the incoming Afghan refugees. These camps became home to a significant portion of the refugee population.
Afghan Civil War: The Soviet withdrawal in 1989 did not bring an end to the conflict in Afghanistan. Instead, the country descended into a brutal civil war among various factions, leading to more Afghans seeking refuge in Pakistan.
Taliban Takeover (1996): In 1996, the Taliban captured Kabul and established their rule in Afghanistan. This led to another wave of refugees, many of whom opposed the Taliban regime.
United Nations Assistance: The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) has been actively involved in assisting Afghan refugees in Pakistan. They provided aid, education, and healthcare services to the refugee population.
9/11 and the War on Terror: Following the September 11, 2001 attacks in the United States, the U.S.-led invasion of Afghanistan in 2001 aimed to remove the Taliban regime and combat terrorism. This had a significant impact on the Afghan refugee situation, as many Afghans returned home, but some continued to seek refuge in Pakistan due to ongoing instability.
Repatriation and Voluntary Return: In the early 2000s, Pakistan, with the support of the UNHCR, initiated a voluntary repatriation program to encourage Afghan refugees to return to their homeland. Many did return, but the situation in Afghanistan remained volatile.
Continuing Challenges: Afghan refugees in Pakistan have faced various challenges, including issues related to legal status, access to education, healthcare, and employment. There have also been periodic government actions to repatriate Afghan refugees.
The situation in Afghanistan remained fluid. The U.S. withdrawal and the Taliban’s return to power have raised concerns about the potential for increased refugee flows into Pakistan and other neighbouring countries.
The Afghan refugee population in Pakistan, which has been present for several decades, has made significant economic contributions to the host country.
While it is challenging to provide precise figures, the economic impact of Afghan refugees in Pakistan can be understood in various ways:
Labour Force and Informal Economy: Afghan refugees have actively participated in Pakistan’s labour force, particularly in low-skilled and manual labour sectors. They have contributed to industries such as construction, agriculture, and services. Many have been employed in informal sectors, filling essential roles in the economy.
Entrepreneurship: Some Afghan refugees have started small businesses and enterprises in Pakistan. This has not only provided them with a source of income but has also created job opportunities for local Pakistanis.
Consumer Spending: Afghan refugees have been consumers in the Pakistani market, contributing to local businesses and boosting demand for goods and services.
Trade and Cross-Border Commerce: Some Afghan refugees have engaged in cross-border trade and commerce, facilitating the flow of goods and contributing to trade between Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Housing and Rental Markets: Many Afghan refugees rent or purchase homes in Pakistan, contributing to the housing and real estate markets. This has had economic implications for the construction and property sectors.
The history of Afghan refugees in Pakistan is marked by both solidarity and challenges. Pakistan has played a critical role in providing shelter to millions of Afghan refugees over the years, but the long-standing presence of a significant refugee population has posed economic, social, and security challenges for the host country.
Over the years, there have been instances of Afghan nationals being involved in terrorist activities in Pakistan. These activities have often been linked to various extremist groups and organizations that have operated in the border region between Afghanistan and Pakistan.
Here are some key points regarding Afghan nationals involved in terrorist activities in Pakistan:
Terrorist Groups: Afghan nationals have been associated with a range of terrorist organizations operating along the Pakistan-Afghanistan border. Some of these groups have targeted both Afghan and Pakistani security forces and civilians.
Cross-Border Movement: The porous and mountainous border between Afghanistan and Pakistan has allowed for the movement of militants and insurgents between the two countries. This has made it easier for militants, including Afghan nationals, to carry out attacks in Pakistan.
Militant Networks: Afghan militants have been part of networks that operate on both sides of the border, often cooperating with local Pakistani militant groups. These networks have been involved in activities such as bombings, assassinations, and other acts of violence.
Efforts to Address the Issue: Both Afghanistan and Pakistan have, at various times, accused each other of harbouring militants and insurgents on their respective territories. The issue has strained diplomatic relations between the two countries.
Counterterrorism Measures: Pakistan has taken various counterterrorism measures, including military operations and intelligence activities, to combat militancy and eliminate terrorist safe havens. This has had implications for both Afghan and Pakistani nationals involved in such activities.
Refugee Population: The presence of a large Afghan refugee population in Pakistan has made it challenging to monitor and control the activities of Afghan nationals, including those with extremist leanings. However, it is important to emphasize that the vast majority of Afghan refugees are not involved in terrorist activities and are seeking refuge from conflict and persecution in their home country.
It’s crucial to recognize that the issue of Afghan nationals involved in terrorism in Pakistan is complex, and the situation has evolved over the years. Efforts to address this issue require cooperation between the governments of Afghanistan and Pakistan, as well as international organizations and the broader international community.