The Pakistani Army has conducted numerous operations against terrorist groups over the years, focusing on regions like the former Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA), Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), and parts of Balochistan.
These operations aim to dismantle terrorist networks, restore law and order, and secure the country’s borders.
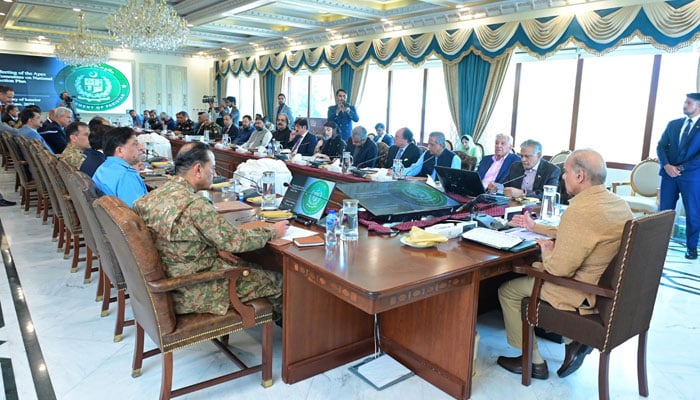
Recently in the Apex committee meeting, Govt approves reinvigorated national counter-terrorism campaign Operation Azm-i-Istehkam. In the Past many military operations have failed to fully eradicate terrorism.
Here’s an in-depth look at some of the most significant military operations:
Operation Zarb-e-Azb (2014)
Objective: To eliminate militant sanctuaries in North Waziristan.
Outcome: The operation resulted in a significant reduction in terrorist activities, dismantling of militant infrastructure, and the restoration of government control in North Waziristan. Thousands of militants were killed or captured, and large caches of arms and ammunition were seized.
Operation Radd-ul-Fasaad (2017)
Objective: To eradicate the residual and latent threat of terrorism, consolidate gains from previous operations, and ensure long-term stability in Pakistan.
Outcome: The ongoing operation has led to continuous counter-terrorism efforts across the country, significant arrests, and the disruption of terrorist networks.
Operation Rah-e-Rast (2009)
Objective: To clear Swat Valley of Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) militants.
Outcome: The operation successfully restored state writ in Swat, facilitated the rehabilitation and resettlement of displaced persons, and rebuilt infrastructure. It significantly weakened TTP’s presence in Swat.
Operation Rah-e-Nijat (2009)
Objective: To eliminate TTP strongholds in South Waziristan.
Outcome: The operation resulted in heavy militant casualties, destruction of militant hideouts, and clearance of the area, reducing TTP’s operational capabilities and control in South Waziristan.
Operation Khyber-IV (2017)
Objective: To target militant groups in the Rajgal Valley of Khyber Agency.
Outcome: The operation successfully cleared the Rajgal Valley and secured the border region with Afghanistan, disrupting cross-border militant movement and safe havens.
Challenges and Considerations
The Pakistani Army’s counter-insurgency efforts are complex due to challenging terrain and deeply entrenched militant groups. Ensuring the safety and rehabilitation of displaced civilians remains a critical aspect of these operations. Regional stability is another key consideration, particularly in relation to Pakistan’s ties with Afghanistan.
Despite notable successes, terrorist groups continue to adapt, necessitating sustained military and intelligence efforts.
Recent Developments
The Pakistani Army remains vigilant, conducting intelligence-based operations to address emerging threats and ensure long-term peace and stability. Coordination with international partners and improved border management are integral to ongoing counter-terrorism efforts.
Despite a series of extensive military operations against terrorist groups, terrorism remains a persistent challenge in Pakistan. These efforts, while successful in many respects, have been unable to completely eliminate the threat. Here’s a look at why these operations have fallen short and what factors continue to fuel terrorism in Pakistan.
Resilience and Adaptability of Terrorist Groups
Terrorist groups like Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) exhibit remarkable resilience and adaptability. They frequently fragment into smaller cells, making them harder to detect and target. After being dislodged from one area, these groups often relocate and re-establish themselves in other regions, including across the border in Afghanistan.
This ability to regroup and adapt has made it difficult for Pakistani military operations to deliver a final blow.
Cross-Border Dynamics Complicate Efforts
The porous border between Pakistan and Afghanistan is a significant challenge. Militants often seek refuge and regroup in Afghanistan, where the presence of safe havens complicates counter-terrorism efforts. Additionally, a lack of effective coordination and intelligence sharing between Pakistan and Afghanistan has historically hampered comprehensive action against cross-border terrorism.
Ideological Appeal and Recruitment Remain Strong
The ideological appeal of extremist groups continues to attract new recruits. Radicalization is facilitated by socio-economic conditions, lack of education, and ineffective governance in certain areas. Furthermore, these groups maintain extensive support networks, including sympathizers who provide logistical, financial, and recruitment support. This ongoing recruitment and radicalization perpetuate the cycle of violence.
Socio-Economic Factors Fuel Extremism
High levels of poverty, unemployment, and lack of opportunities make it easier for terrorist groups to recruit disenfranchised youth. Insufficient socio-economic development and governance in certain regions create environments conducive to the operations of terrorist groups. Addressing these root causes is crucial for long-term stability.
Political Instability and External Influences
Frequent political instability and changes in government policies can disrupt sustained counter-terrorism efforts. Moreover, foreign involvement and geopolitical interests in the region also play a role in exacerbating the terrorist threat. These internal and external political factors further complicate efforts to maintain security.
Challenges in Law Enforcement and Intelligence
Law enforcement agencies in Pakistan often face resource constraints, limiting their ability to conduct effective counter-terrorism operations. Despite improvements, there are still gaps in intelligence gathering, sharing, and analysis, which hinder preemptive action against terrorist threats. Strengthening these capacities is essential for a more effective response.
Rehabilitation and Integration Issues
Effective rehabilitation and reintegration programs for former militants are crucial but often underfunded or poorly implemented. Winning the hearts and minds of local populations through sustained development and security measures is essential to undermine the influence of terrorist groups. Long-term strategies are needed to ensure these individuals do not return to militant activities.
Judicial System Challenges
Weaknesses in the judicial system, including inadequate protection for judges and witnesses, lead to low conviction rates for terrorists. Ensuring a robust legal framework to support counter-terrorism efforts while respecting human rights is a delicate balance that is still evolving. Strengthening the judicial system is key to sustaining counter-terrorism gains.
Conclusion
While military operations in Pakistan have significantly weakened many terrorist groups and improved security in several regions, the multifaceted nature of terrorism requires a comprehensive approach. Addressing underlying socio-economic issues, enhancing regional cooperation, strengthening law enforcement and judicial systems, and fostering ideological counter-narratives to combat radicalization are crucial for long-term success. Only through a holistic strategy can Pakistan hope to fully eradicate the scourge of terrorism and ensure lasting peace and stability.